[Tips] Optuna를 이용한 hyper parameter optimization
이 포스트는 아래 원문의 내용을 참고하여 번역 및 수정한 것이다. 원문을 보고 싶으면 아래 링크에서 확인할 수 있다.
원문:
A 5 min guide to hyper-parameter optimization with Optuna
전체코드:
이 게시물에서는 간단한 pytorch 신경망 훈련 스크립트를 가져와 Optuna 패키지(docs here )를 이용하여 성능을 향상 시킬 것이다.
먼저 Pytorch를 이용하여 간단한 MNIST 분류 스크립트를 짜본다. 이 스크립트를 조금 수정하여 Optuna를 이용한 이퍼 파라미터 최적화를 해본다.
1. Vanilla MNIST Classifier Framework
먼저 필요한 module을 import하고 data loader를 만드는 것으로 시작한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
from __future__ import print_function
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
def get_mnist_loaders(train_batch_size, test_batch_size):
"""Get MNIST data loaders"""
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST('../data', train=True, download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])),
batch_size=train_batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST('../data', train=False, transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])),
batch_size=test_batch_size, shuffle=True)
return train_loader, test_loader
다음으로는 간단한 네트워크를 구현한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, activation):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, 3, 1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, 1)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout2d(0.25)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout2d(0.5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(9216, 128)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, 10)
self.activation = activation
def forward(self, x):
x = self.activation(self.conv1(x))
x = self.conv2(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
x = self.dropout1(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.activation(self.fc1(x))
x = self.dropout2(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
output = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
return output
학습에 필요한 train 과 test 메서드를 구현한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
def train(log_interval, model, train_loader, optimizer, epoch):
model.train()
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data.to(device)
loss = F.nll_loss(output, target.to(device)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch_idx % log_interval == 0:
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset),
100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item()))
def test(model, test_loader):
model.eval()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data, target in test_loader:
output = model(data.to(device)
test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target.to(device), reduction='sum').item() # sum up batch loss
pred = output.argmax(dim=1, keepdim=True) # get the index of the max log-probability
correct += pred.eq(target.to(device).view_as(pred)).sum().item()
test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)
test_accuracy = 100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset))
print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'.format(
test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),
100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))
return test_accuracy
return
main 함수는 아래와 같이 구현한다. 하이퍼 파라미터는 cfg 변수 안에 선언하였다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
def train_mnist():
cfg = { 'device' : "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu",
'train_batch_size' : 64,
'test_batch_size' : 1000,
'n_epochs' : 1,
'seed' : 0,
'log_interval' : 100,
'save_model' : False,
'lr' : 0.001,
'momentum': 0.5,
'optimizer': optim.SGD,
'activation': F.relu}
torch.manual_seed(cfg['seed'])
train_loader, test_loader = get_mnist_loaders(cfg['train_batch_size'], cfg['test_batch_size'])
model = Net(cfg['activation']).to(device)
optimizer = cfg['optimizer'](model.parameters(), lr=cfg['lr'])
for epoch in range(1, cfg['n_epochs'] + 1):
train(cfg['log_interval'], model, train_loader, optimizer, epoch)
test_accuracy = test(model, test_loader)
if cfg['save_model']:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "mnist_cnn.pt")
return test_accuracy
if __name__ == '__main__':
train_mnist()
2. Enhancing the MNIST classifier framework with Optuna
Optuna 프레임워크를 아래의 명령어를 이용하여 설치한다. Optuna는 Study 개체를 기반으로 한다. 이 개체에는 필요한 파라미터 공간에 대한 정보와 sampler 방법과 pruning에 대한 모든 정보가 포함되어 있다.
1
pip install optuna
study은 아래의 방법으로 생성할 수 있다.
1
2
import optuna
study = optuna.create_study(sampler=optuna.samplers.TPESampler(), direction='maximize')
study가 만들어진 후 search space는 trial.suggest_ 메서드를 통해 포함된다. 이것을 위에서 정의한 train_mnist 내부에 있는 config에 삽입한다. 위에서 정의한 configuration을 다음과 같이 수정한다.
1
2
3
'lr' : 0.001,
'momentum' : 0.5,
'optimizer': optim.SGD,
1
2
3
'lr' : trial.suggest_loguniform('lr', 1e-3, 1e-2),
'momentum' : trial.suggest_uniform('momentum', 0.4, 0.99),
'optimizer': trial.suggest_categorical('optimizer',[optim.SGD, optim.RMSprop]),
trial에 사용할 수 있는 함수는 이 링크를 참고한다.
- uniform — float values
- log-uniform — float values
- discrete uniform — float values with intervals
- integer — integer values
- categorical — categorical values from a list
만약 epoch을 설정하고 싶다면 아래의 명령어처럼 설정해주면 된다.
1
'n_epochs' : trial.suggest_int('n_epochs', 3, 5, 1), #3~5 에폭, step은 1
위의 방법으로 search space를 정의한 후 train_mnist() 메서드가 trial 을 입력으로 받도록 해야 한다. 따라서 train_mnist(trial) 로 바꿔준다. trial 외의 것을 입력으로 받아야 한다면 그 방법에 대해서는 해당 링크를 참조한다.
최종적으로 train_mnist 함수는 다음과 같이 될 것이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
def train_mnist(trial):
cfg = { 'device' : "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu",
'train_batch_size' : 64,
'test_batch_size' : 1000,
'n_epochs' : trial.suggest_int('n_epochs', 3, 5, 1),
'seed' : 0,
'log_interval' : 100,
'save_model' : False,
'lr' : trial.suggest_loguniform('lr', 1e-3, 1e-2),
'momentum' : trial.suggest_uniform('momentum', 0.4, 0.99),
'optimizer': trial.suggest_categorical('optimizer',[optim.SGD, optim.RMSprop]),
'activation': F.relu}
torch.manual_seed(cfg['seed'])
train_loader, test_loader = get_mnist_loaders(cfg['train_batch_size'], cfg['test_batch_size'])
model = Net(cfg['activation']).to(device)
optimizer = cfg['optimizer'](model.parameters(), lr=cfg['lr'])
for epoch in range(1, cfg['n_epochs'] + 1):
train(cfg['log_interval'], model, train_loader, optimizer, epoch)
test_accuracy = test(model, test_loader)
if cfg['save_model']:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "mnist_cnn.pt")
return test_accuracy
3. Optimization
마지막 단계로 최적화 될 objective function을 정의한다. 이 포스트의 경우는 train_mnist 를 objective function으로 정하였고, 그 결과인 test error를 최적화 하도록 한다.
따라서, study.optimized 안에 train_mnist 함수를 파라미터로 넣어준다.
1
2
study.optimize(train_mnist, n_trials=20, direction='maximize')
joblib.dump(study, '/content/gdrive/My Drive/Colab_Data/studies/mnist_optuna.pkl')
train_mnist() 를 호출하기 위한 전체적인 main 코드는 다음과 같이 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
sampler = optuna.samplers.TPESampler()
study = optuna.create_study(sampler=sampler)
study.optimize(train_mnist, n_trials=20, direction='maximize')
joblib.dump(study, '/content/gdrive/My Drive/Colab_Data/studies/mnist_optuna.pkl')
위의 라인이 코드에 추가되면 optimizer는 샘플러에 따라 (예시에서는 TPESampler) 정의 된 매개 변수 공간을 샘플링한다.
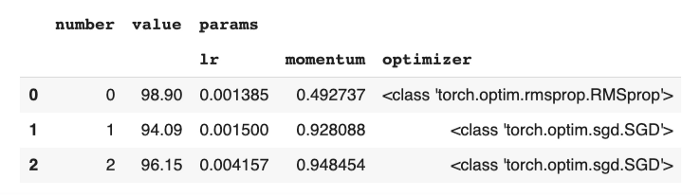
최적화가 완료된 후 결과는 다음을 통해 데이터 프레임으로 액세스 할 수 있다 study.trials_dataframe :
1
2
3
4
from sklearn.externals import joblib
study = joblib.load('/content/gdrive/My Drive/Colab_Data/studies/mnist_optuna.pkl')
df = study.trials_dataframe().drop(['state','datetime_start','datetime_complete','system_attrs'], axis=1)
df.head(3)
그러면 다음과 같은 결과가 출력될 것이다.
최적의 파라미터를 확인하기 위해서 study.best_trial및 study.best_params도 사용할 수 있다.
위의 방법으로 최적화를 한 후에 동일한 양의 학습 데이터와 동일한 시간으로 98.9 % 테스트 오류 (~ 6 % 개선) 결과를 얻을 수 있었다.
4. Visualization
최적의 파라미터를 찾는 것 외에도 Optuna를 통해 시각화 할 수 있다. 모든 시각화 툴은optuna.visualization 에 포함되어 있다.
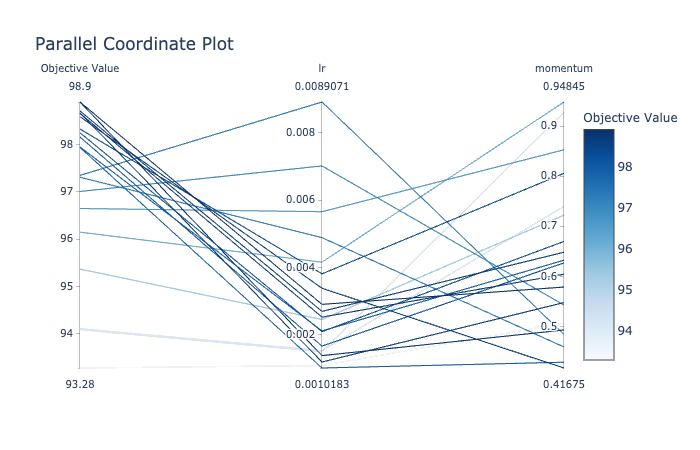
예를 들어 파라미터 간의 관계를 확인하기 위해 plot_parallel_coordinates(study) 이라는 명령어를 사용하여 아래와 같은 결과를 얻을 수 있다. (이 예시에서는 lr과 momentum이 파라미터)
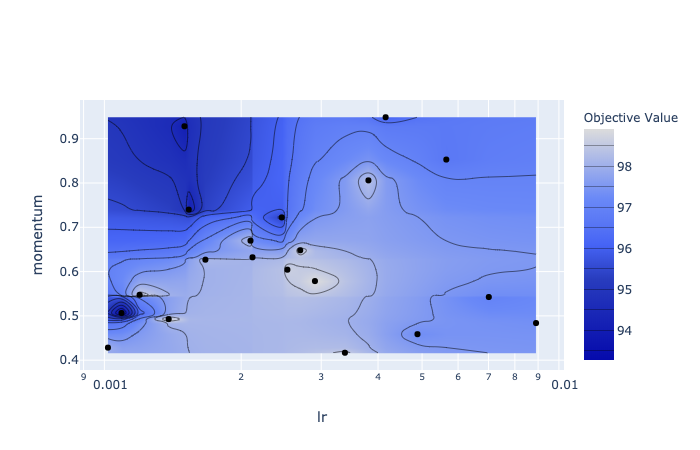
다른 방법으로 contour plot을 이용할 수도 있다. 이 결과는 plot_contour(study) 를 통해 얻을 수 있다.
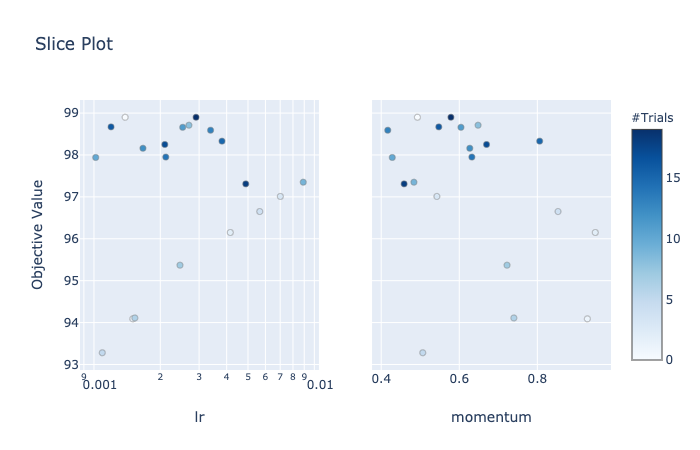
또한 slice_plot(study) 을 호출하여 slice plot을 만들 수 있다. 이는 각 파라미터에 대해 개별적인 최적의 부분 공간이 어디에 위치하는지 이해하는 데 도움이 될 수 있다.
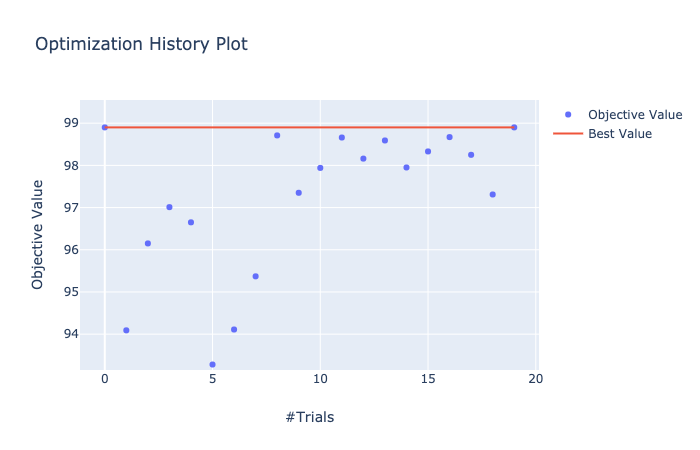
마지막으로 study history를 시각화 하기 위해 plot_optimization_history(study) 을 이용할 수도 있다.
5. 요약
- 실제 학습에 사용되는 함수를 수정한다. (예시에서
train_mnist함수가 이에 해당한다. ) 이 함수는 아래의 조건을 충족해야 한다.- 평가 지표가 될 점수를
return해야 한다. 이 함수 안에서 모델의 파라미터를 정해준다. (trial.suggest_..함수 이용) - 이 함수는
trial을 매개변수로 받아야 한다.
- 평가 지표가 될 점수를
study.optimize를 실행한다. 1에서 정의한 함수를 파라미터로 넘겨준다. 예시:study.optimize(train_mnist, n_trials=20, direction='maximize')
6. 참고
[1] https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-make-your-model-awesome-with-optuna-b56d490368af